10 Uses of Stethoscope in HealthCare & Checkups

The stethoscope is an essential medical instrument used by healthcare professionals worldwide to listen to internal sounds produced within the human or animal body. This versatile tool has multiple features that allow doctors to examine a patient’s condition through various body sounds. In this blog, we will explore the top 10 uses of stethoscope, discussing their importance in diagnosing and treating patients.
1 How to use a Stethoscope?
Using a stethoscope is relatively straightforward, but it does require some practice to master the technique. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use a stethoscope:
Choose the right stethoscope: Select a stethoscope that meets your needs, with options including acoustic, electronic, and specialized stethoscopes such as those for paediatrics or cardiology. Ensure the stethoscope has comfortable ear tips and a high-quality chest piece for optimal sound transmission.
Prepare the patient: Have the patient sit straight with their back supported and expose the area you want to examine. Make sure the patient is relaxed and comfortable, as this can affect the sounds you hear.
Hold the stethoscope correctly: Grasp the chest piece in your dominant hand, with your index and middle fingers on the diaphragm or bell. Hold the earpieces with your other hand so they point forward and align with your ear canals.
Insert the earpieces: Gently insert the earpieces into your ears, ensuring a snug fit to block out external noise. The earpieces should be angled slightly forward to match the direction of your ear canals for optimal sound transmission.
Place the chest piece on the patient’s body: Depending on what you are examining (heart, lungs, abdomen, etc.), gently place the chest piece on the appropriate area of the patient’s body. For heart and lung sounds, position the chest piece on the patient’s chest, avoiding the nipple line and bony structures.
Switch between the diaphragm and bell: The diaphragm is used for listening to high-pitched sounds, such as normal breath and heart sounds. The bell is better suited for low-pitched sounds, like heart murmurs and some vascular sounds. To switch between them, apply light pressure for the diaphragm and firmer pressure for the bell.
Listen carefully: Take your time and focus on the sounds you hear. Compare the sounds on the left and right sides of the patient’s body, as well as different locations, to ensure a comprehensive assessment.
Adjust the chest piece as needed: As you listen to different body sounds, you may need to reposition the chest piece or adjust the pressure applied to capture the best sound quality.
Document your findings: Record the sounds you heard, any abnormalities, and other relevant observations. This information is crucial for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Clean the stethoscope: After each use, clean the chest piece and ear tips with a disinfectant wipe to maintain hygiene and prevent cross-contamination.
Remember that using a stethoscope effectively takes practice. Over time, you will become more adept at the first stethoscope, identifying various sounds and differentiating between normal and abnormal findings.
2 10 Uses of Stethoscope
Listening to Heart Sounds
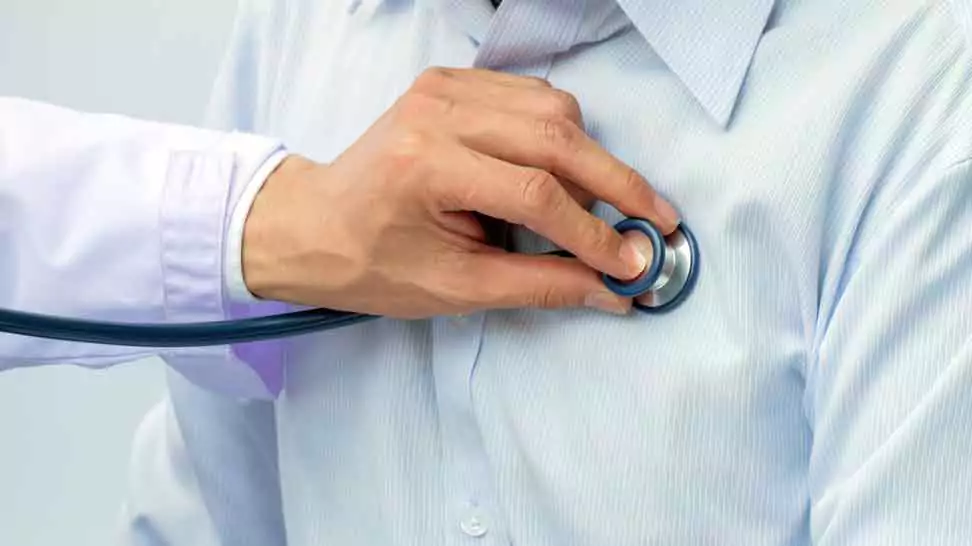

A stethoscope with chest pieces is used to listen to a patient’s heart, enabling healthcare providers to determine if it is beating correctly. By placing the chest piece on the patient’s chest, doctors can detect abnormal heart sounds, such as heart murmurs, that may indicate underlying issues. The acoustic stethoscope is particularly useful for identifying low-pitched sounds, while electronic stethoscopes can amplify faint sounds, ensuring accurate diagnosis.
Assessing Lung Sounds
Another vital use of the stethoscope is to evaluate a patient’s respiratory system by listening to lung sounds. Healthcare professionals can place the chest piece on various points of the patient’s chest and back to identify abnormalities such as wheezing, crackles, or decreased breath sounds. These unusual sounds can be indicative of respiratory illnesses or conditions which may require further investigation.
Monitoring Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is a critical health indicator, and the stethoscope plays a significant role in its measurement. By using a blood pressure cuff and listening to the brachial artery, healthcare providers can measure blood pressure accurately. As the cuff deflates, Korotkoff sounds are produced, allowing doctors to calculate blood pressure by identifying the systolic blood pressure measurement and diastolic pressure points.
Evaluating Bowel Sounds
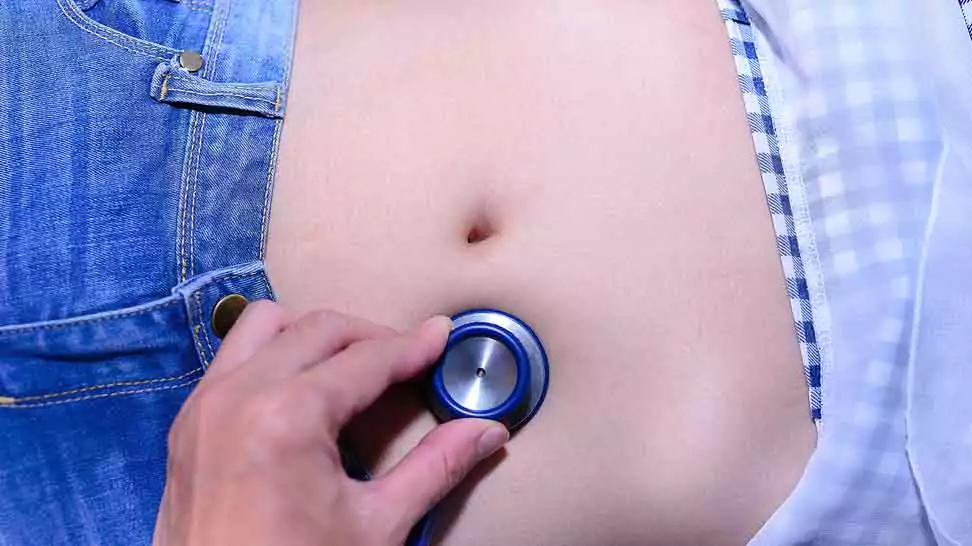

The stethoscope can also be used to listen to bowel sounds, enabling healthcare professionals to identify potential gastrointestinal issues. Bowel blockages, inflammation, or other abnormalities can create high-pitched or abnormal abdominal sounds that can be detected by placing the chest piece on the patient’s abdomen. This non-invasive method allows for a quick assessment and can help guide further diagnostic tests if needed.
Detecting Blood Flow
Another essential function of the stethoscope is to monitor blood flow within the body. By placing the chest piece over the patient’s arteries, such as the carotid or temporal arteries, doctors can listen for any unusual sounds that may indicate a blockage or other circulatory issues. The Doppler stethoscope, in particular, is useful for detecting blood flow disturbances, making it a valuable tool in vascular assessments.
Measuring Liver Size
A lesser-known use of the stethoscope is in measuring liver size. Doctors can use the stethoscope’s diaphragm to percuss the patient’s body, listening for changes in sound waves as they move from the lungs to the liver. This technique can help healthcare providers estimate the liver size and identify potential abnormalities or enlargements that may require further investigation.
Assessing for Arterial Stenosis

Arterial stenosis, or narrowing of the arteries, can be detected by a doctor using a stethoscope to listen for abnormal sounds called bruits. Healthcare professionals can place the chest piece over the patient’s arteries and identify these unusual sounds, which can indicate the presence of arterial stenosis. Early detection and intervention are crucial for preventing complications associated with this condition.
Evaluating Joint Sounds
The electronic stethoscope can also be used to assess joint sounds, allowing healthcare providers to detect potential issues within the musculoskeletal system. By placing the chest piece over a patient’s joints and having them move the joint, doctors can listen for abnormal sounds, such as crepitus or grinding noises, which may indicate joint dysfunction or damage.
Monitoring Fetal Heart Beat
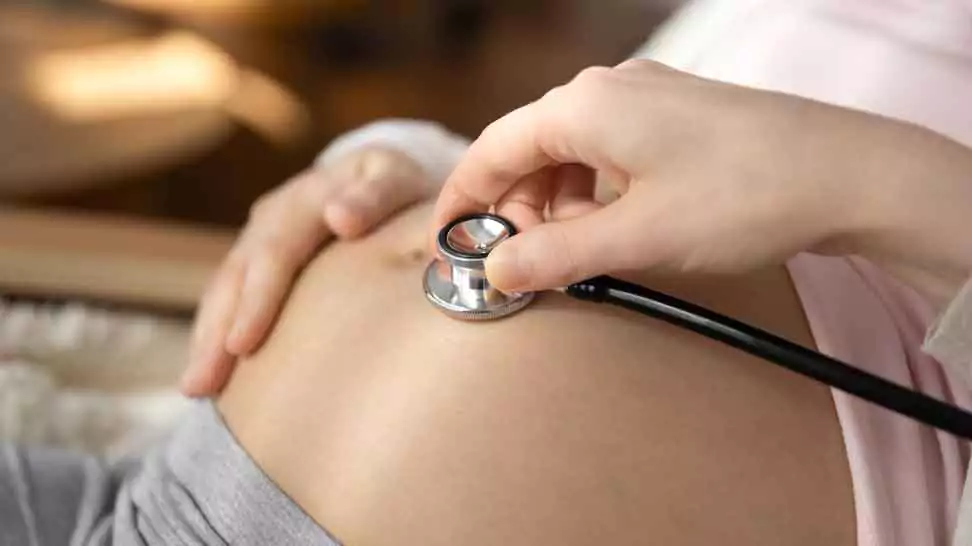
Prenatal care is essential for ensuring the health of both the mother and baby and the stethoscope plays a crucial role in this process. By using a specialized fetal stethoscope, healthcare providers can listen to the fetal heartbeat, monitor the heartbeat rate, and detect any abnormalities that may require further evaluation. This non-invasive method allows doctors to assess the baby’s condition and make necessary interventions if needed.
Veterinary Applications
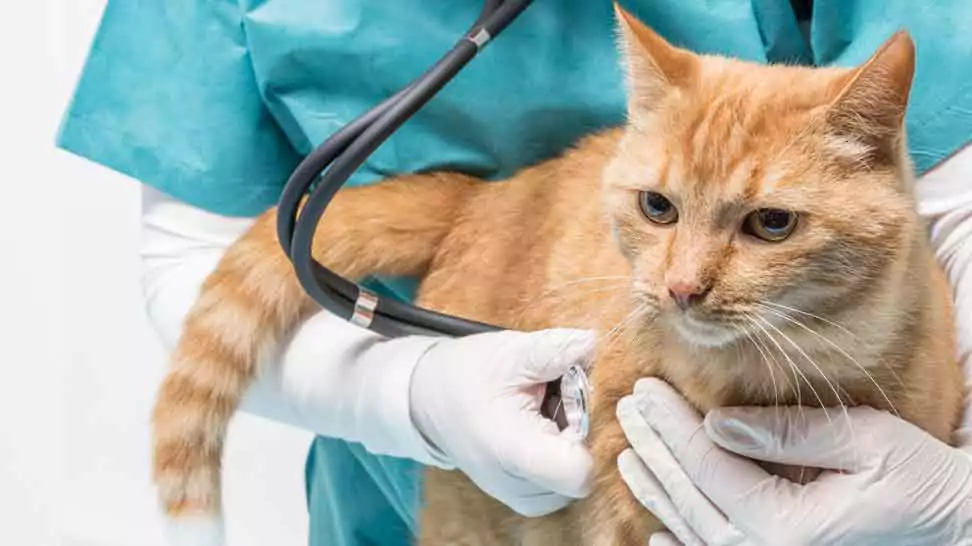
Stethoscopes are not limited to human use; they are also valuable tools for veterinary healthcare professionals. In examining animals, veterinarians can use the stethoscope to listen to the heart, lungs, and other internal sounds of various species, assisting in diagnosing and treating a wide range of animal health issues.
3 Wrapping Up
The stethoscope is an indispensable medical instrument for healthcare professionals, offering a simple yet effective method for assessing a patient’s body and detecting potential health issues. From monitoring blood pressure and evaluating lung sounds to measuring liver size and detecting arterial stenosis, the stethoscope’s versatility makes it a critical tool in providing accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Throughout this blog, we have discussed the many uses of the stethoscope, including the ability to detect unusual or abnormal sounds, the importance of acoustic and electronic stethoscopes, and the various applications within both animal and human bodies. With its rich history and continued advancements, the stethoscope remains a vital component of healthcare, ensuring that doctors and other healthcare providers can offer the best possible care to their patients.
Community Q&A
About This Article
This article has been viewed 968 times.



