How Many Types of Printer are Available in the Market?
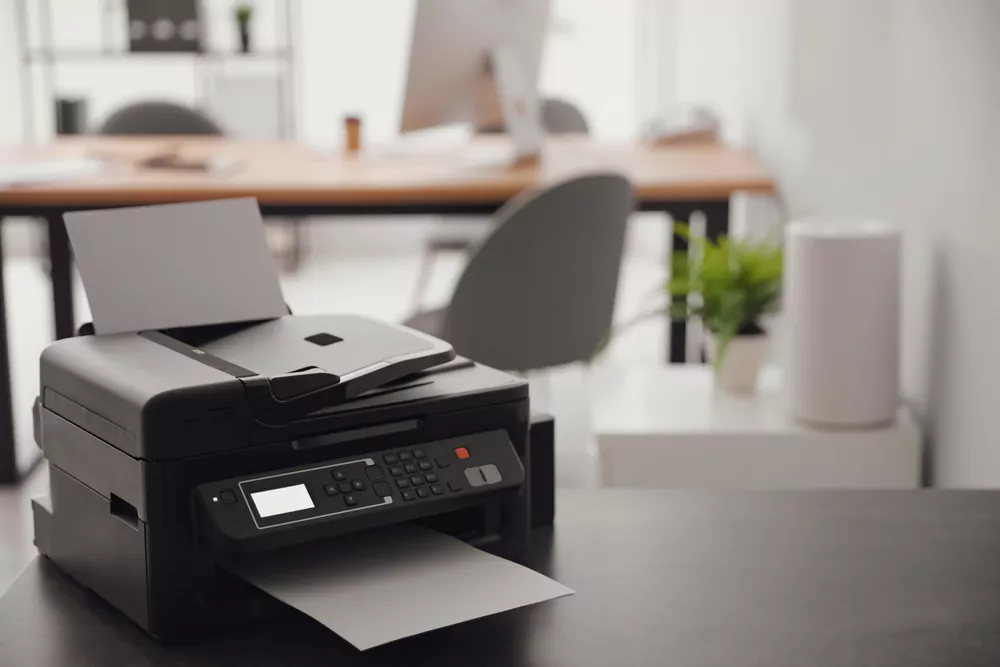

In today’s fast-paced world, having a reliable printer at your disposal is essential, whether you work from home or run a business. With an overwhelming number of options available in the market, the question “How many types of printer” are there can be confusing. This comprehensive guide will explore various how many types of printers are there currently, their features, benefits, and drawbacks to help you decide when purchasing your next printer.
1 Types of Printer
Inkjet Printers
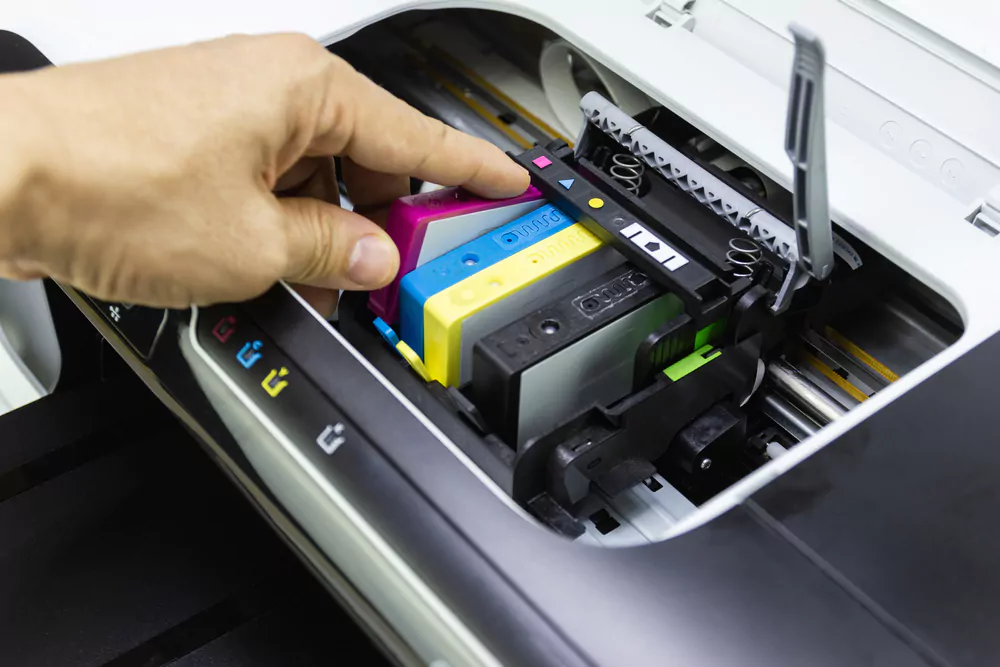

Inkjet printers are one of the most common types of printers available in the market. These printers use liquid ink stored in cartridges, sprayed onto paper in tiny droplets through a series of nozzles. Inkjet printers are versatile, capable of producing high-quality text documents, photos, and graphics.
- High-quality colour printing.
- The affordable, upfront cost.
- Compact design suitable for home and small office use.
- Slower print speed compared to laser printers.
- Ink cartridges can be expensive, resulting in a higher cost per page.
- Prone to smudging if the ink is not given time to dry.
Laser Printers
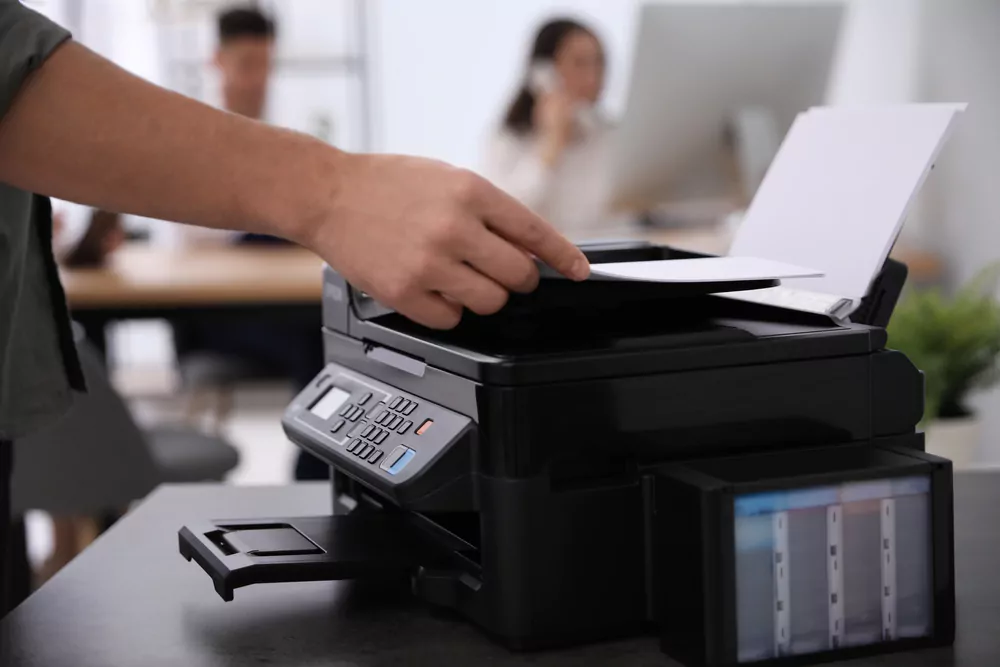

Laser printers use a laser beam to create an electrostatic image on a drum, which then transfers toner onto the paper. This method results in fast, high-quality prints, making laser printers a popular choice for businesses and large offices. Laser printers are available in monochrome and colour models.
- Fast print speeds.
- Lower cost per page compared to inkjet printers.
- Excellent text quality.
- Higher upfront cost.
- Larger sizes may not be suitable for smaller spaces.
- Colour laser printers can be expensive.
Solid Ink Printers
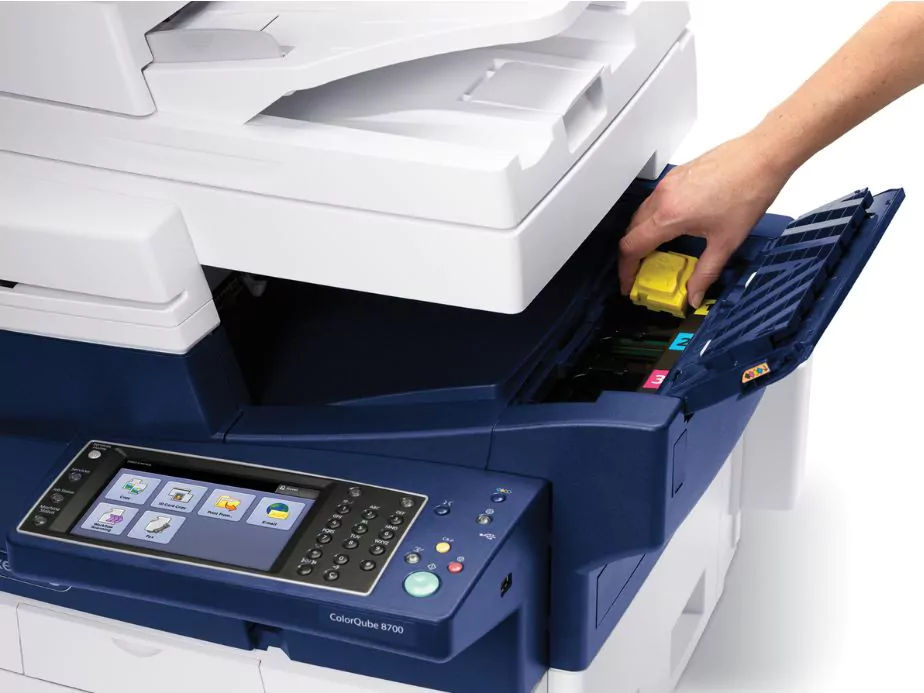

Solid ink printers use a unique technology that melts solid ink sticks and sprays the ink onto a drum before transferring it to paper. This type of printer is less common but offers a few advantages over traditional inkjet and laser printers.
- Vibrant and saturated colours.
- Environmentally friendly due to less waste from cartridges.
- Compact design.
- Slower print speed compared to laser printers.
- Ink sticks can be expensive.
- Limited availability and brand options.
Thermal Printers
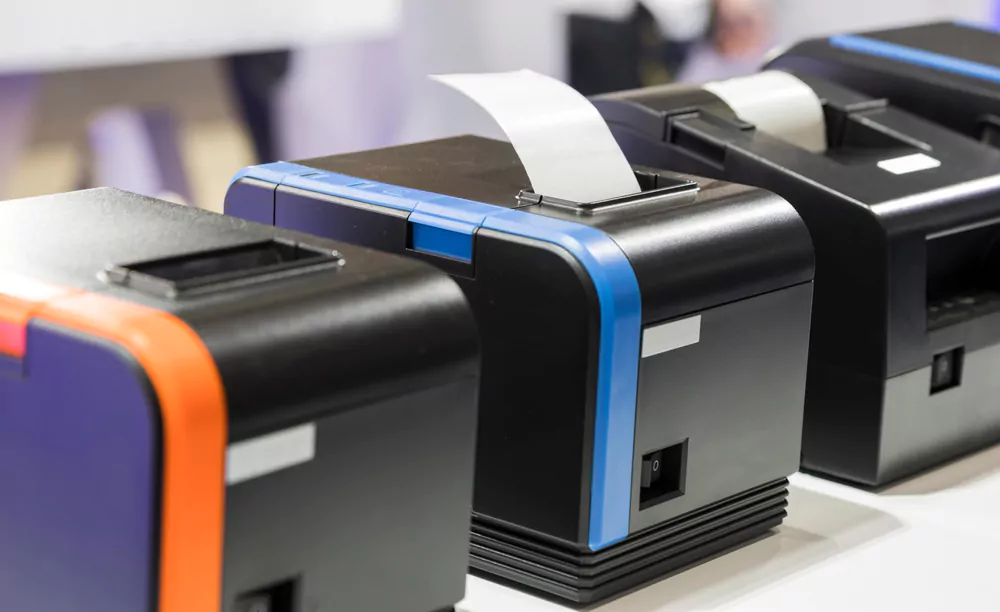

Thermal printers use heat to transfer ink from a ribbon onto the paper. These printers are commonly used for label printing, barcode printing, and receipt printing. There are two main types of thermal printers: direct thermal and thermal transfer.
- Fast print speeds.
- Low maintenance, as no ink or toner is required.
- Compact design suitable for point-of-sale systems.
- Limited to printing on thermal paper.
- Print quality may degrade over time.
- Not suitable for high-quality photo or document printing.
Dot Matrix Printers
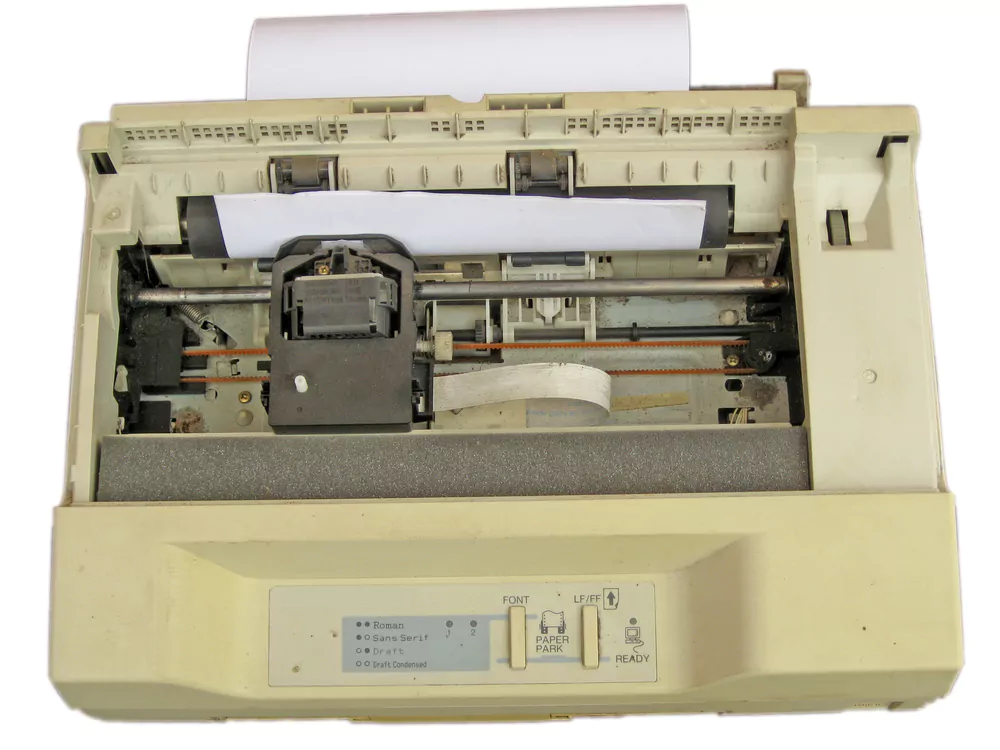
Dot matrix printers, also known as impact printers, use a print head that moves across the paper and strikes an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against it, forming characters or images with tiny dots. Although dot matrix printers are less common today, they are still used in specific applications where continuous paper or multi-part forms are required.
- Low cost per page.
- Can print on multi-part forms and continuous paper.
- Durable and long-lasting.
- Noisy operation.
- Lower print quality compared to inkjet and laser printers.
- Slow print speeds.
Dye-Sublimation Printers
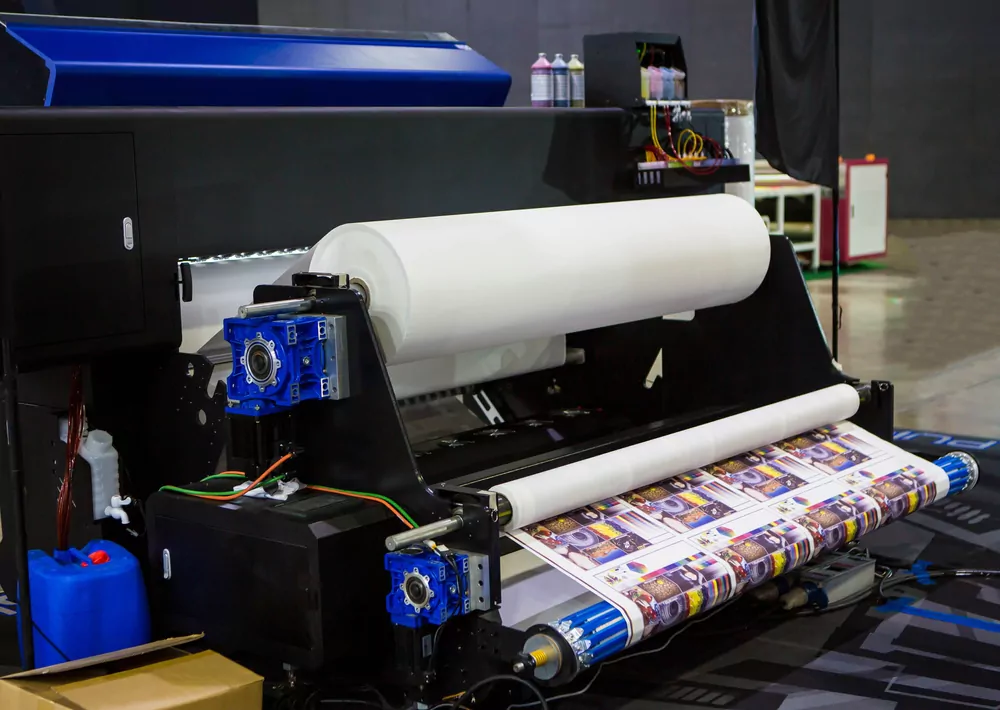

Dye-sublimation printers use heat to transfer dye onto various materials, such as paper, fabric, or plastic. These printers are primarily used for photo printing and are popular for professional photography applications.
- High-quality photo prints with continuous tone.
- Durable and fade-resistant prints
- Can print on various materials.
- Expensive consumables, such as dye-sublimation paper and ribbons.
- Slower print speeds compared to inkjet and laser printers.
- Limited to specific applications, such as photo printing.
Wide-Format Printers
Wide-format printers, also known as large-format printers or plotters, are designed to print on large sheets of paper or other materials, such as vinyl or canvas. These printers are typically used for printing banners, posters, blueprints, and other large-scale projects.
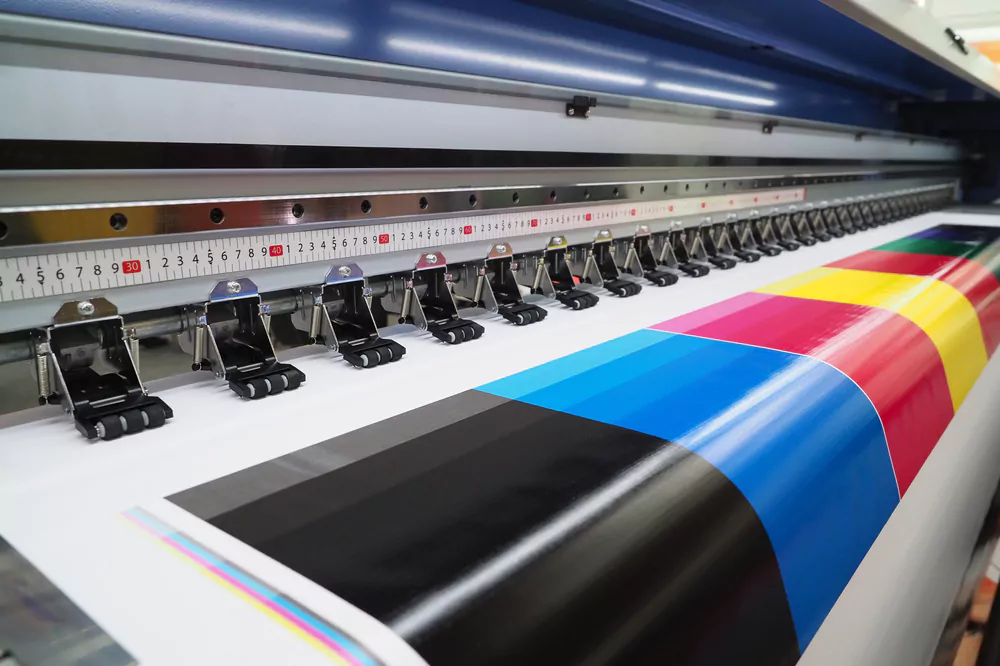

- Can print on various materials, including paper, vinyl, and canvas.
- Capable of printing large sizes for signage, blueprints, and posters.
- High-quality printing for graphics and images.
- Expensive upfront cost.
- Large size requires ample workspace.
- Consumables, such as ink and media, can be costly.
3D Printers
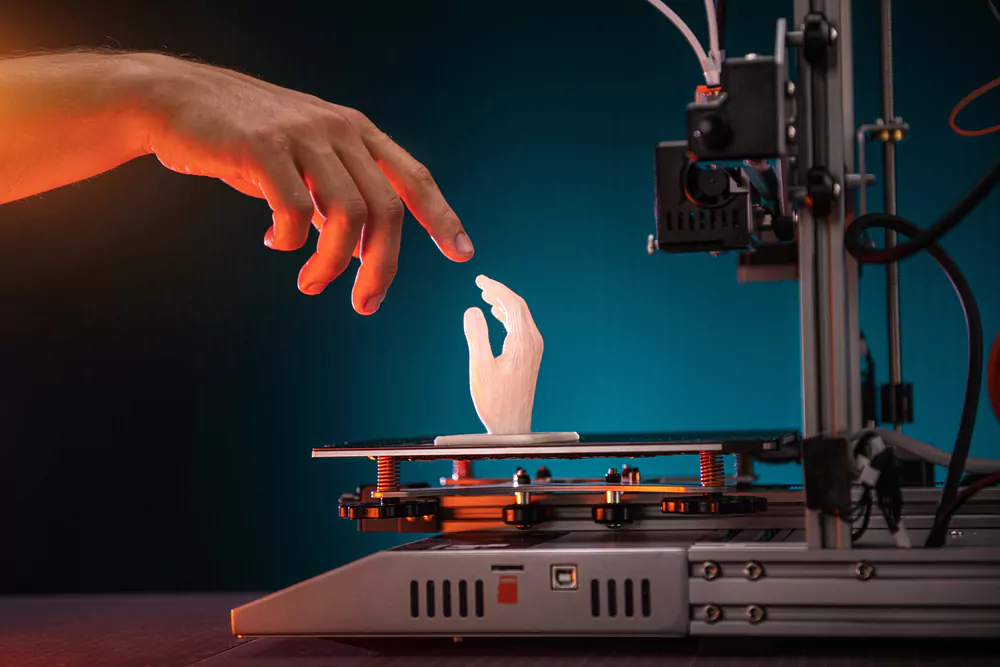

3D printers create three-dimensional objects by depositing material layer by layer based on a digital model. These printers have gained popularity in recent years for various applications, such as prototyping, manufacturing, and even creating art pieces or household items.
- Ability to create complex, three-dimensional objects.
- Wide range of applications, from prototyping to art.
- Customisation options for unique, personalised creations.
- Expensive upfront cost, particularly for professional-grade models.
- Requires specialised software and knowledge to operate.
- The printing process can be time-consuming.
2 Wrapping Up
Understanding how many types of printers are available in the market and their respective features, benefits, and drawbacks is crucial when selecting the right printer for your needs. Whether you require high-quality photo prints, fast document printing, or specialised printing on various materials, there is a printer type designed to meet your requirements.
When choosing a printer, consider factors such as print quality, speed, cost per page, and the type of materials you will be printing on. By carefully considering your specific needs and researching the different types of printers available, you can make an informed decision and invest in a printer that will serve you well for years to come. To simplify this task for you, We have hand-picked some of the best printers under 10000.
Community Q&A
About This Article
This article has been viewed 526 times.



