Parts of a Refrigerator and Their Functions

A refrigerator is an integral part of our daily lives, ensuring our food remains fresh and edible for longer. When considering how a refrigerator works, it’s essential to understand its various parts and their respective functions. Dive into this comprehensive guide to explore the cooling agent and myriad internal and external parts of a refrigerator and their functions that collectively ensure peak performance.
1 The Basic Refrigeration Cycle
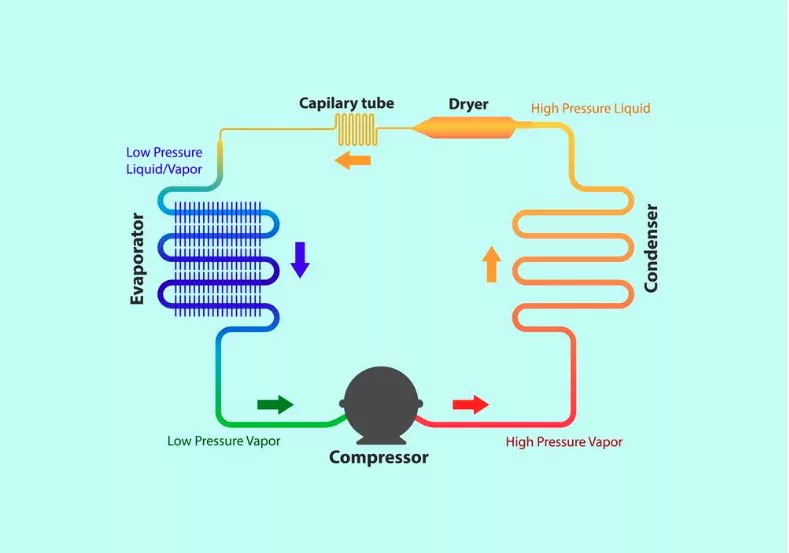
At its core, the refrigeration cycle involves a cooling agent or refrigerant that undergoes various phase changes—converting from gas to liquid and vice versa—to cool the air inside the refrigerator and freezer compartments.
Evaporator Coils
The cooling process starts with the evaporator coils. These coils house the liquid refrigerant. As the refrigerant passes through the evaporator coils, it evaporates, turning from a liquid state to vapor. This phase change allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the surrounding air inside the fridge, thereby cooling it. The cool air then circulates through the refrigerator and freezer compartments via small vents, keeping your food items cold and fresh.
Compressor
The vapor refrigerant, now holding the absorbed heat, is transported to the compressor. This component pressurizes the gaseous refrigerant, increasing its temperature.
Condenser Coils
The high-pressure, high-temperature gaseous refrigerant then moves to the condenser coils, typically located at the back or underneath most refrigerators. These coils release the heat to the outside air, causing the refrigerant to condense. This heat rejection transforms the gaseous refrigerant back into its liquid form.
Expansion Device
After the condensation process, the liquid refrigerant flows through an expansion device—either a capillary tube or an expansion valve—which drops the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, causing it to cool further.
Once the refrigerant completes this cycle, it returns to the evaporator coils, and the process repeats.
2 Key Parts and Their Roles
Condenser and Evaporator Coils
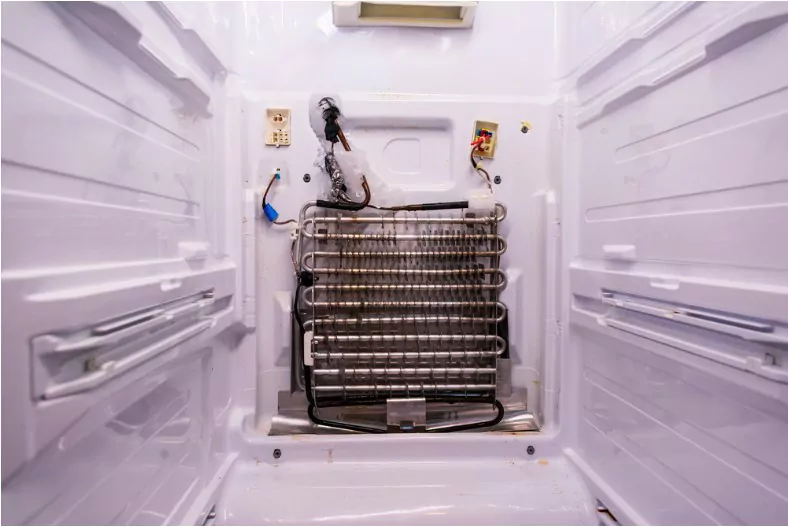

We’ve touched upon their pivotal roles in the refrigeration system. The evaporator coils absorb heat from the inside, while the condenser coils release heat outside. The seamless transition between the two is what keeps the temperature inside at an optimal range.
Thermostat Control
This component senses the temperature inside the refrigerator and freezer compartments. When the temperature rises, it signals the compressor to start, initiating the refrigeration cycle.
Freezer Compartment
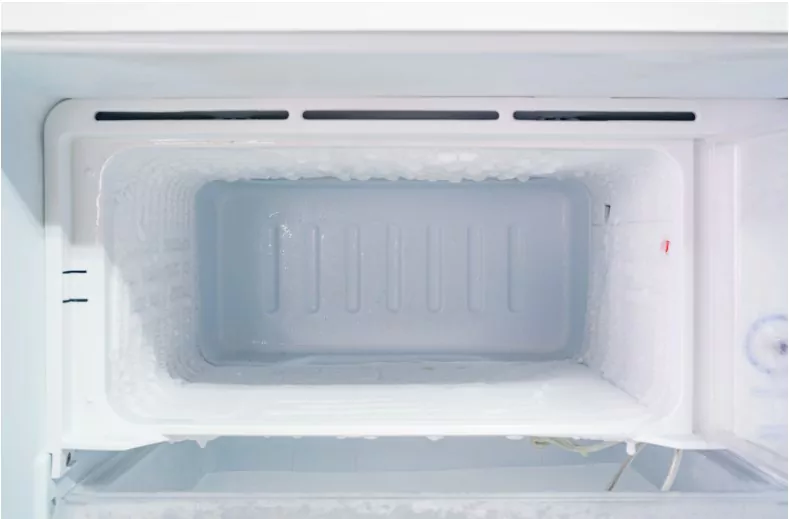

While most understand its function—to freeze and store food—it’s also essential in the cooling process for the rest of the refrigerator. The evaporator coils are often located here, and as the liquid refrigerant absorbs heat, ice gets formed in the freezer, making the environment colder.
Refrigerant
This cooling agent undergoes phase changes, alternating between liquid and gas states, to absorb and release heat. Its ability to change forms under different pressure and temperature conditions is vital to the cooling process.
3 The Liquid and Vapor Dance
The transition of the refrigerant between its liquid and vapor forms is the essence of how a refrigerator works. The cycle of compression, heat rejection, expansion, and heat absorption keeps our food cooled, ensuring it remains fresh for longer periods.
4 The Importance of Maintenance and Replacement
As with any device, some parts wear out over time, impacting the refrigerator’s efficiency. Regular maintenance ensures all the refrigerator parts, both internal and external, are in good condition.
Should a component fail, it’s reassuring to know that refrigerator replacement parts are typically available. Regularly inspecting parts like the condenser and evaporator coils and ensuring there’s no obstruction to the flow of air will prolong the life of your fridge.
5 Wrapping Up
Refrigerators are marvels of engineering, using principles of physics to cool our food and keep it fresh. Understanding how they work demystifies the process and can help us appreciate them even more. Whether it’s the complex dance between the condenser and evaporator coils, the phase changes of the refrigerant, or the crucial role of the thermostat control, each part and function is essential to the refrigerator’s overall performance.
By ensuring regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn-out parts, we can extend the lifespan of our refrigerators and continue to enjoy fresh, cool food items daily.
When next you open your refrigerator, think of the intricate processes that occur behind the scenes, from the heat absorption in the evaporator coils to the heat rejection in the condenser coils, all to ensure that your food stays fresh and cold. Cheers to the wonders of modern refrigeration!
Community Q&A
About This Article
This article has been viewed 433 times.



