The Truth about Can Processor be Changed in Laptop?
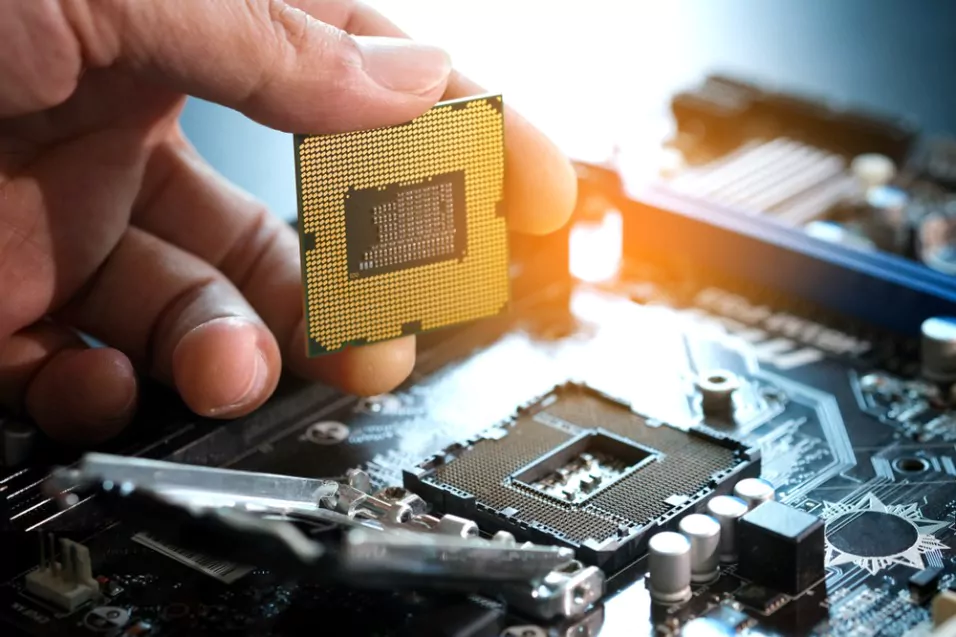
In recent years, laptops have become a necessary tool for work and personal use. As laptops have become more popular, the demand for more processing power has also increased. Laptops come equipped with processors, which are the brains of the machine, responsible for executing instructions and handling calculations. However, as new and more powerful processors are released, many people wonder if it is possible to change a laptop’s current processor anyway. In this blog post, we will explore the possibilities of changing a laptop’s processor and what factors need to be considered.
- What is a Laptop Processor?
- Can you change a laptop processor in most modern laptops?
- How to check processor compatibility?
- How to change a laptop processor?
- Step 1: Research compatible processors
- Step 2: Gather the necessary tools
- Step 3: Prepare the laptop
- Step 4: Open the laptop's casing
- Step 5: Locate the processor
- Step 6: Remove the old processor
- Step 7: Install the new processor
- Step 8: Apply thermal paste
- Step 9: Reassemble the laptop
- Step 10: Power up and test
- Wrapping Up
1 What is a Laptop Processor?
A laptop processor, also known as a laptop CPU, is a small chip that is responsible for executing instructions and handling calculations on a laptop. The processor is one of the most important components in a laptop, as it determines the speed and efficiency of the computer. Modern laptops usually come equipped with Intel Core i5 processors, which are the most popular type of processor in the market.
2 Can you change a laptop processor in most modern laptops?
The short answer is yes, you can change the laptop’s processors. However, there are some factors that need to be considered before doing so. The first factor is the laptop model, as not all laptops are designed to have their processors changed. Some laptops have their processors soldered to the motherboard, which means they cannot be removed. If your laptop has a soldered processor, you will not be able to change it.
The second factor to consider is the socket type. The socket type is the physical interface that connects the processor to the computer’s motherboard. The socket type varies depending on the processor model, and not all sockets are compatible with each other. Before changing your laptop’s processor, you need to make sure that the new processor you want to install is compatible with your laptop’s socket type.
3 How to check processor compatibility?
To check processor compatibility, you need to know your laptop’s processor socket type. You can usually find this information in the laptop’s manual or by searching online for the laptop model’s specifications. Once you know your laptop’s processor socket type, you can then search for compatible processors. Intel Desktop CPUs provide a CPU support site where you can enter your processor socket number and find compatible processors.
What factors affect laptop processor compatibility?
The most important factor that affects laptop processor compatibility is the socket type. The socket type varies depending on the processor model, and not all sockets are compatible with each other. The second factor that affects processor compatibility is the same processor and motherboard’s socket number. The motherboard’s socket number must match the socket type of the new processor for it to be compatible. If the motherboard’s socket number and the new processor’s socket type do not match, the processor will not fit or work correctly.
Another factor that affects processor compatibility is the laptop’s cooling system. More powerful processors generate more heat, so if you want to install a more powerful processor, you need to make sure that your laptop’s cooling system can handle the increased heat output. If your laptop’s cooling system is not sufficient, the new or upgraded processor may overheat, causing damage to the laptop.
What are the benefits of changing a laptop processor?
The main benefit of changing a laptop’s processor is increased processing power. If you install a more powerful processor, your laptop will be able to handle more demanding tasks, such as video editing or gaming. This increased processing power can improve the overall performance of your laptop and make it run faster.
Another benefit of changing a laptop’s processor is cost savings. If you want to upgrade your laptop’s processing power, you may be considering buying a new laptop. However, by changing your laptop’s processor, you can save money and still enjoy the benefits of a more powerful machine.
What are the risks of changing laptop processors?
The main risk of changing a laptop’s CPU processor is damaging the laptop. Changing a laptop’s processor requires a high degree of technical knowledge, and if not done correctly, it can cause permanent damage to the laptop. Additionally, if the new processor is not compatible with the laptop’s socket type or cooling system, it can cause the laptop to overheat, which can also cause permanent damage.
Another risk of changing a laptop CPU socket is voiding the laptop’s warranty. The manufacturers of most laptops void the warranty if any components are tampered with or replaced. If you change your laptop’s processor, you may be voiding the warranty, which means that if any other components fail, you will have to pay for the repairs yourself.
4 How to change a laptop processor?
Upgrading your laptop’s processor can improve its performance significantly, especially if you’re using an older model with a slower CPU. However, changing a laptop processor can be a complex process, and it’s not recommended for novice users. It requires a certain level of technical knowledge and experience, and any mistake can damage the laptop’s hardware irreversibly.
Here are the steps you need to follow to change a laptop processor:
Step 1: Research compatible processors
Before you start the process of changing your laptop’s processor, you need to research and find out which processors are compatible with your laptop’s new motherboard. You can check your laptop manufacturer’s website to see if they provide information about which processors are compatible with your laptop’s motherboard.
Step 2: Gather the necessary tools
You’ll need a few tools to replace your laptop’s processor, including a screwdriver, thermal paste, and a grounding strap or mat. You can buy these items at most computer hardware stores. You’ll need a few tools to replace your laptop’s processor, including a screwdriver, thermal paste, and a grounding strap or mat. You can buy these items at most computer hardware stores.
Step 3: Prepare the laptop
To prepare the laptop, shut it down and unplug it from any power source. Remove the battery from the laptop, and disconnect any other cables or components that may be attached to it.
Step 4: Open the laptop's casing
To access the processor, you’ll need to remove the laptop’s casing. The casing may be held in place by screws or clips, so you’ll need to remove them carefully. Make sure you keep track of where each screw or clip goes so that you can reassemble the laptop correctly.
Step 5: Locate the processor
Once you’ve removed the motherboard tab the casing, locate the processor on the motherboard. It should be a small square chip with several pins protruding from it.
Step 6: Remove the old processor
To remove the old processor, carefully unclip or unscrew the heat sink that covers it. The heat sink helps to dissipate the heat generated by the processor, so it’s important to remove it carefully. Once you’ve removed the heat sink, gently lift the old processor out of its socket.
Step 7: Install the new processor
Take your new processor out of its packaging and align it with the socket on the motherboard. Make sure the pins on the processor are aligned with the socket, and gently press it into place.
Step 8: Apply thermal paste
Once the new processor is in place, apply a small amount of thermal paste to the top of the processor. The thermal paste helps to conduct heat from the surface mounting type processor to the heat sink, so it’s important to apply it evenly.
Step 9: Reassemble the laptop
Once you’ve applied the thermal paste, reattach the heat sink to the processor and secure it in place. Then, carefully reassemble the laptop casing, making sure to reattach all screws and clips in the correct locations.
Step 10: Power up and test
Once you’ve reassembled the laptop, power it up and test the new processor’s performance. You can run benchmarking software to see how well the laptop is performing and whether the new processor has improved its performance.
5 Wrapping Up
Changing a laptop’s processor is possible, but it is not recommended for beginners or those without technical knowledge. Before changing your laptop’s processor, you need to consider the laptop model, socket type, and cooling system. Changing a laptop’s processor can increase processing power and save money, but it also comes with risks, such as damaging the laptop or voiding the warranty. If you are unsure about changing your laptop’s processor, it is recommended to seek professional help.
Community Q&A
About This Article
This article has been viewed 643 times.



