A Complete Guide to What is Laser Printer?

In a world of rapidly evolving technology, laser printers have become an integral part of our daily lives. From homes to offices, these printers are known for their speed, efficiency, and high-quality prints. But what is laser printer, and how does it work? In this blog post, we will unravel the mystery behind laser printers, discuss their advantages and disadvantages, and explore their various applications.
1 Understanding Laser Printers: The Basics
“What is a laser printer?” – this is a question we often encounter when discussing printing technology. A laser printer is a type of non-impact printer that uses laser beams to create images or text on paper. It works by creating a static electrical charge on a drum (or photoconductor), which then attracts toner particles to form the desired image or text. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat and pressure, resulting in a crisp and clear printed output.
2 The History of Laser Printers
The invention of laser printers can be traced back to the 1960s when Xerox researcher Gary Starkweather had the revolutionary idea of using a laser beam to create images on paper. In 1971, Starkweather and his team developed the first-ever laser printer, called the Xerox 9700 Electronic Printing System. Initially, laser printers were massive, expensive, and limited to specialised applications. However, the introduction of more affordable personal laser printers in the 1980s by companies like HP and Canon made them accessible to a wider audience, and they soon became popular for both personal and professional use.
3 How Laser Printers Work
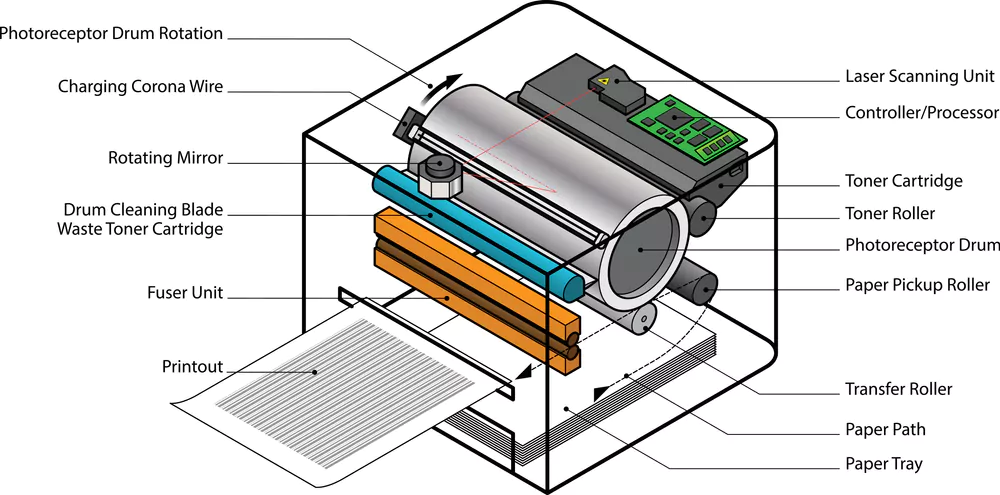
To understand what a laser printer is, it’s essential to know how it works. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the laser printing process:
Data Processing: When you send a document to the printer, the printer’s built-in processor converts the data into a raster image format, which is a matrix of tiny dots (pixels) that represent the image.
Charging: Inside the printer, there’s a photosensitive drum (or photoconductor) that rotates as the printing process begins. The drum is first given a uniform negative electrical charge by a corona wire or charging roller.
Exposing: A laser beam is used to “write” the image onto the drum by discharging the areas that correspond to the image or text. This creates a pattern of charged and discharged areas on the drum, which represent the image to be printed.
Developing: The drum then passes by the toner cartridge, which contains positively charged toner particles. The charged areas on the drum attract the toner particles, effectively transferring the image onto the drum.
Transferring: The drum comes into contact with the paper, which has been given a positive charge by another corona wire or transfer roller. This causes the toner particles to transfer from the drum onto the paper.
Fusing: Finally, the paper passes through a fuser assembly, which uses heat and pressure to melt and bond the toner particles onto the paper permanently.
Cleaning: After the printing process, the drum is cleaned of any residual toner and recharged, ready for the next print job.
4 Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Printers
Laser printers come with their own set of pros and cons, which can influence your decision when choosing a printer for your needs:
Advantages
- High speed: Laser printers are generally faster than inkjet printers, making them ideal for high-volume printing tasks.
- High print quality: Laser printers produce sharp, high-resolution images and text, resulting in professional-looking documents.
- Lower cost per page: Although laser printers may have higher upfront costs, the cost per page is usually lower compared to inkjet printers, especially when printing in large volumes.
- Less maintenance: Laser printers typically require less frequent maintenance and have fewer components to replace, such as ink cartridges and printheads.
- Reliability: Laser printers are known for their durability and can handle large workloads, making them suitable for busy office environments.
Disadvantages
- Higher initial cost: The upfront cost of a laser printer is generally higher than that of an inkjet printer.
- Limited colour capabilities: While colour laser printers are available, they may not produce the same vibrant colours and photo-quality prints as high-end inkjet printers.
- Bulky size: Laser printers are usually larger and heavier than inkjet printers, which can be a disadvantage in small or cramped spaces.
- Power consumption: Laser printers consume more power than inkjet printers, which can lead to increased energy costs.
- Environmental concerns: The toner used in laser printers can be harmful to the environment, as it contains non-biodegradable materials.
5 Applications of Laser Printers
Now that we have answered the question, “What is a laser printer?” and discussed its advantages and disadvantages, let’s look at some common applications of laser printers:
- Office use: Laser printers are widely used in offices due to their speed, efficiency, and ability to handle high-volume printing tasks. They are ideal for printing documents, reports, and other text-heavy materials.
- Graphic design: Laser printers are suitable for graphic design purposes, as they can produce sharp, high-resolution images and crisp text. However, for the highest quality colour prints and photographs, professional graphic designers may still prefer inkjet printers.
- Home use: Laser printers are becoming increasingly popular for home use due to their reliability, low cost per page, and high print quality. They are suitable for everyday printing tasks, such as homework assignments, invoices, and personal documents.
- Small businesses: Small businesses can benefit from the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of laser printers, especially those that require high-volume printing and professional-looking documents.
- Education: Schools and educational institutions often use laser printers for their speed, efficiency, and ability to produce large quantities of printed materials, such as worksheets, handouts, and exams.
6 Wrapping Up
Understanding what a laser printer is, how it works, and its applications can help you make an informed decision when choosing the right printer for your needs. Laser printers are known for their speed, efficiency, and high-quality prints, making them ideal for various settings, from homes to offices. However, they do come with some disadvantages, such as higher initial costs and limited colour capabilities compared to inkjet printers. By weighing the pros and cons and considering your specific needs, you can select the best printing solution for your home, office, or business.
Community Q&A
About This Article
This article has been viewed 518 times.



